Saturday, March 9, 2019
Friday, March 1, 2019
II YEAR ANALOG & DIGITAL IC-APPLICATIONS IMP QUESTIONS
ANALOG AND DIGITAL IC-APPLICATIONS
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
UNIT 1: (OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS)
ESSAYS:
1. Define an op-amp ? what are the ideal characteristics of an op-amp and explain the block diagram of an op-amp?
2. Explain the working of inverting and non-inverting op-amp?
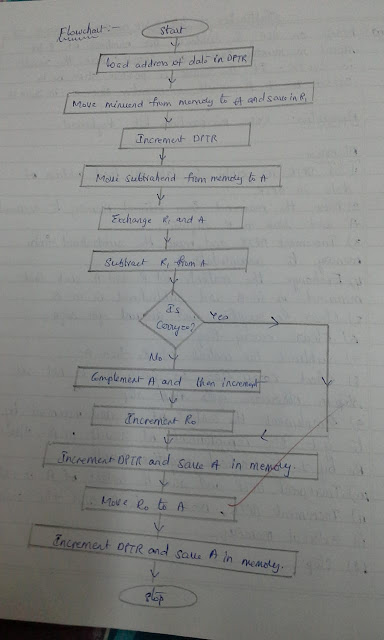
3. Explain the working of integrator and differentiator op-amp ?
4. Explain the op-amp acts as logarithmic amplifier and differential amplifier ?
5. Explain the op-amp acts as summing amplifier and subtractor amplifier ?
6. Explain the op-amp parameters ?
SHORTS:
7. Explain the concept of virtual ground ?
8. Explain the op-amp acts as voltage follower ?
9. Explain the op-amp acts as voltage to current convertor ?
10. Explain the working of non- inverting adder op-amp?
UNIT 2: (OP-AMP CIRCUITS)
ESSAYS:
1.Explain the working of Astable multivibrator (or) free running multivibrator
by using op-amp ?
by using op-amp ?
2. Explain the working and analysis of Monostable multivibrator by using op-amp ?
3. Explain the working of sine wave generator (or) wein bridge oscillator by using op-amp ?
4.Explain the functional block diagram of IC-55 timer and mention it’s applications?
4.Explain the functional block diagram of IC-55 timer and mention it’s applications?
5. Explain the op-amp acts as instrumentational amplifier ?
6. Explain the frequency response of low pass and high pass filters by using op-amp ?
SHORTS:
7. Explain the op-amp acts as comparator ?
8. Explain the op-amp acts as voltage regulator ?
9. Explain the op-amp acts as zero crossing detector ?
10. Explain the working of Bi-stable multivibrator by using op-amp ?
11. Explain the op-amp acts as Schmitt trigger ?
12. Explain the working of triangular wave generator by using op-amp ?
13. . Explain the band pass filter by using op-amp ?
UNIT 3:(IC-APPLICATIONS)
ESSAYS:
1.Explain the design of BCD to Seven segment code convertor ?
2. Explain the design of BCD to Grey code convertor ?
3. Explain the design of Grey to binary code convertor ?
4. Explain the design of universal shift register ?
5. Explain the design of binary up/down counter ?
SHORTS:
SHORTS:
6. Explain the design of Mod N counter ?
7. Explain the design of preset table ?
UNIT 4: (DATA CONVERTERS)
ESSAYS:
1.Explain the Successive Approximation method of ADC?
2.Explain the Sigma to delta method of ADC?
3.Explain the R-2R ladder network method of ADC?
4.Explain the Binary weighted method of ADC?
SHORTS:
5.Write a short note on Single slope method of ADC?
6.Write a short note on dual slope method of ADC?
7.Explain the Characteristics of DAC?
UNIT 5: (DIGITAL SYSTEM INTERFACING & APPLICATIONS)
ESSAYS:
1.Explain the Interfacing of LED's?
2.Explain the construction & working of Digital clock?
3.Explain the construction & working of UART?
SHORTS:
4. Write a short note on Parallel to Serial Shift Register?
5.Write a short note on Serial to Parallel Shift Register?
Sunday, February 24, 2019
embedded product development life cycle
*** Explain
Embedded product development life cycle?
Embedded product development life cycle is an “Analysis-Design –Implementation” based standard problem solving approach for Embedded product Development.
In any product development
application, we consider
1.What product needs to be developed
(Analysis)
2. Good approach for building it (design)
3. To develop it ( Implementation).
EDLC is an Analysis-Design-implementation
based problem solving approach for embedded systems development.
Analysis involves
understanding what product needs to be developed.
Design involves
what approach to be used to build the product.
Need
for EDLC :
1. EDLC
is essential for understanding the scope
(fesilities) and complexity of the work involved in embedded systems
development.
2. It
is used for any developing embedded product.
3. EDLC
defines interaction and activities among various groups of a product
development phase.
***
Discuss about objectives of EDLC
1.
The ultimate aim of any embedded product in a
commercial production setup is to produce Marginal benefit.
2.
Marginal is expressed in terms of ROI ( Return
On Investment).
3.
The investment for product development
includes initial investment, manpower, infra structure investment etc.
EDLC
has three primary objectives :
1. Ensuring
high quality for products.
2. Risk
minimization and Defect prevention through Management.
3. Maximize
the productivity.
Ensuring
high Quality for products:
Quality in any product development is Return On Investment (ROI) achieved by the product.
The expenses for developing the product are
1.
Initial Investment
2.
Developer recruiting.
3.
Training
4.
Infra structure requirement.
Risk minimization defect prevention in product
development through project management
Product
development “loose” or “tight” project management.
“project management is essential for
“predictability co-ordination and risk minimization.
Place
the resources is critical and having a direct impact on investment.
Eg: Microsoft @ project Tool.
Maximize
the productivity ;
Productivity
is a measure of efficiency as well as Return On Investment (ROI).
This productivity measurement is
based on total man power efficiency.
Productivity in which, when, product is
increased then investment is fall down. Saving man power.
Phases
of EDLC.
NEED
Phase:
The “need” may come from individual (or) from the public (or) from a company.
The “need” may come from individual (or) from the public (or) from a company.
“Need” should be initiate the “Development
Life Cycle”
“Need “ can be visualized in any one of the 3
Needs :
1. New (or) Custom product Development.
2. Product Re-engineering
3. Product Maintenance.
Conceptualization phase:
It defines the scope of concept.
It performs cost benefit analysis and prepare project management and risk
management plans & feasibility study.
Activities
in conceptualization:
1.
Feasibility study :
Examine the need and suggest possible solutions.
2.
Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) : Revealing
and assessing the total development cost and profit expected from the product.
3.
Product scope : Deals
with the activities involved in the product to be made.
4.
Planning Activities: It
requires various plans to be developed first, before development like resource
planning & Risk management plans.
Analysis
Phase :
The product is defined in detailed with respect to the inputs, processes,
outputs and interfaces at a functional level.
Activities
in Analysis:
1.
Analysis
& Documentation: It specifies the business needs of the
product under development.
2.
Requirements
that need to be addressed.
·
Functional capabilities like performance.
·
Operational & Non-operational quality
attribute.
·
Product external interface requirements.
·
Data requirements, user manuals
·
Operational requirements.
·
Maintenance requirements
·
General assumptions.
Defining
Test plan and procedures phase :
In product development there are various
types of testing is performed they are
◊ Unit
testing : Testing individual modules
◊ Integration
Testing : Testing a group of modules for required functionality.
◊ System
Testing : Testing functional aspects
(or) functional requirements of the
product after integration.
◊ User
acceptance testing : Testing the
product to meet the end user requirements.
Design
phase:
It identifies application
environment and creates an over all architecture for the product.
§ It
starts with the preliminary Design.
§ It
establishes the top level architecture for the product.
§ On
completion it resembles a “black box” , that defines only the inputs and outputs.
§ The
final product is called preliminary Design Document (PDD)
§ After
PDD the end user create the “Detailed Design”.
§ The
operational manual design, maintenance manual design, product Training material
Design all together called the “Detailed Design Document”.
Development
and Testing Phase:
Development means designing the particular product into hardware and software.
Testing can be divided into independent testing of software &
Hardware .
v Unit
testing
v Integration
testing
v System
testing
v User
acceptance testing
Deployment
Phase:
Deployment is the process of
launching the first
fully
functional model of the product in the market.
It is also known as first customer shipping
(FCS)
Support phase:
The support deals with the
operational & maintenance of the product in the production environment.
Activities
involved in support phase
It providing 24x7 supports for the product after launching.
Identify the areas of improvement.
Upgrades Phase:
Deals
with the development of up grades (new version) for the product, which is
already present in the market.
During the upgrade phase the system is
subject to design modification in major areas.
Retirement/Disposal;
The
retirement/disposal of the product is a gradual process.
This phase is the final phase in a product
development life cycle.
The
product is declared as discontinued from the market.
The
disposal of a product is essential due to
1.
Increased user needs.
2.
Rapid technology advancement.
The
trends in the embedded systems
1.Processor Trends:
1.Processor Trends:
There is a points of difference between the first
generation of processor/controller and today’s processor/controller.
2.
Number of IC’s per chip;
Early processors has few number of IC/gates
per chip.
Today’s processors with VLSI technology
can pack (together) ten of thousands of IC/gates per processor.
3.Need
for individual components:
Early processors need different components
like timers, DAC/ADC separately interfaced.
Today’s processors have all these components
on the same chip as the processor.
4. Speed
of execution:
Early processors were slow
in execution speed.
Today’s processor with
advanced architecture support features like instruction pipeline, improving the
execution speed.
5.Clock Frequency:
Early processors execute at few MHz.
Today’s processors are capable of execute at
GHz range.
6.Application
Specific Processor:
Early systems designed available at that
time.
Today
it is possible according to a product requirement.
7.Major
Trends in Processor architecture in Embedded development.
System On-Chip (SOC) :
This concept makes possible to integrate all functional systems required
to build an embedded product into a single chip.
SOC are now available for a wide variety of diverse applications as
Media players, PDA etc.
SOC integrate multiple
functional components on the same chip.
8.Multicore processors/Chip level Multi
processor:
This concept specifies multiple cores on the same
processor chip, operating at the same clock frequency and battery.
Based on the number of cores
:
v Dual
core-2 cores
v Tri
core-3cores
v Quad
core-4 cores.
Each core implements pipelining and multi
threading.
9. Reconfigurable processors:
It is a hardware feature.
Depending on the requirement, re configurable processors can change their
functionality to the new requirement.
Eg: The heart of a camera, Media player.
10.Operating
system Trends:
The
advancements in processor technology caused a major change in the Embedded
operating System Industry.
There are lots of options for Embedded operating System to select both
commercial and open source.
Virtualization concept is used in embedded OS industry.
11. Development Language Trends:
There are two aspects to Development
languages w.r.to Embedded systems Development.
i.
Embedded
Firmware:
It is application to responsible for execution
of Embedded System.
It is the software to perform low level hardware interaction , memory
management.
ii Embedded Software;
It is the software that is responsible
for interfacing with the Embedded System.
It is the user application that executes on top of the Embedded system
on a Host Computer.
Early languages available for Embedded systems development were limited,
they are C & C++ only.
Now ASP,▪
NET , VB, Java are available.
12. Open
Standards, Frame works and Alliances:
Standards are necessary for ensuring inter
operation.
Open Source Standards and frame works
Specific to the mobile hand set industry.
OMA (Open Mobile Alliance) is a
standard body for creating open standards for mobile industry.
The Goal of OMA is deliver High Quality.
OHA (Open Handset Alliance) is
a group of 84 technology and mobile companies.
Eg:
Andriod, Openmoko.
13.
Bottlenecks faced by Embedded industry
Memory performance
The
rate at which processors can process their memory speed increasing.
Lack
of Standards/conformance to Standards
Lack of skilled Resource.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)