***Explain OVER VIEW of 8051
Microcontroller (OR) Explain basic functional blocks of a Microcontroller
·
The Microcontroller is a Programmable IC by VLSI Technique and capable of performing
Arithmetic and Logical operations.
·
The basic functional blocks of a
microcontroller are ALU, Flag register, Register array, Program Counter (PC),
Instruction decoder, Timing and control Unit, RAM memory, EPROM/EEPROM memory,
Parallel I/O port, Serial I/O port, programmable timer, ADC & DAC. But all
the microcontrollers may not have all the blocks.
·
In
microcontroller ALU performs
arithmetic and logical operations.
·
Flag
Register: The various
conditions of the result are stored as status bits in flag register.
·
Register
array & Internal RAM memory are used as temporary storage
device for storing temporary data during execution of a program.
·
EPROM/EEPROM:
The
program codes and permanent data are stored in EPROM/EEPROM.
·
In microcontroller based systems external memory is provided when
internal memory is not sufficient.
·
Program
Counter : The program counter generates the address of the
instructions to be fetched from the memory and send to the memory.
o
The micro controllers communicate with
external world only through I/O Ports.
o
The instruction codes are decoded by instruction decoding Unit and send information to timing and
Control Unit.
o
The
timing & Control Unit will generate the necessary control
signals for internal and external operation of the microcontroller.
o
The parallel
and Serial I/O Ports are used for interfacing I/O devices like Switches,
Keyboard, LCD/LED, ADC, DAC ect. and also for any other input/output
operations.
o
The microcontrollers does not have dedicated
external address and data bus. Therefore for interfacing any additional Peripheral devices, the external address and data buses
are using port lines.
o
The microcontrollers with internal ADC can directly accept analog signals for processing.
o
The microcontroller with internal DAC can directly
generate analog signals for
controlling analog devices.
§ The programmable timer can be used for time
based operations and it can also be used as a counter.
*** Explain the features of
8051 Microcontroller.
Features of 8051:
·
4096 bytes On-Chip program memory.
·
128 bytes On-Chip data memory .
·
Four register banks.
·
128 User-defined Software flags.
·
64 K bytes each program and external RAM
addressability.
·
One microsecond instruction cycle with 12MHz
crystal.
·
32 Bi directional I/O lines organized as four
8-bit Ports.
·
Multiple mode, High-speed programmable Serial
port.
·
Two multiple mode, 16-bit Timers/Counters.
·
Two-level prioritized interrupt Structure.
·
Full depth Stack for subroutine return
linkage and data storage
·
Direct byte and bit address ability
·
Binary
or decimal arithmetic
·
Signed-overflow detection and parity
computation
·
Hardware multiple and divide in 4 µsec
*** Explain the Architecture
of 8031/8051 (OR) Function of block (OR)
Register organization (OR) Block diagram.
The
various functional blocks of 8051 are ALU, Special function Registers (SFR) ,
Instruction Register (IR), Program Counter (PC), 128 bytes RAM, 4 Kb ROM, Port latches and
drivers, oscillator, Timing & Control Unit.
The
8031/8051 has Harvard Architecture
it has same address in different memory device or banks for using program and
data
It
has two16- bit pointers one is program counter (pc) it is used as address pointer
To
access program instructions and it is automatically incremented after every
byte of instruction fetch.
Second one is data
pointer ( DPTR) it is used as address pointer to read /write data in data
memory and it is programmable using instructions .
By
using this 16- bit pointers we can
address 216 =64 Kb. Memory
locations. Hence 8051/8031 supports two memory banks of 64 Kb each, one for program
and the other for data.
EA (External access)
Used to read program from external memory.
When EA bar is connected to ground (logic-0) then entire 64Kb is used
as external (EPROM/RAM) memory.
If we want to read from external
memory then EA bar is connected to GND that means EA=5V or 1.
If we use only internal memory then we connect EA bar to Vcc (5V)
Means EA=0V.
When
EA bar is connected to Vcc (logic-1) the first 4 Kb of program
memory is refer to internal ROM (4Kb) & remaining 60Kb is to external
(EPROM/RAM). Memory.
8051
has separate 256 bytes internal RAM( by 8-bit address). In 256 bytes, first 128
bytes are allotted for internal RAM and next 128 bytes are to SFR.
It
has four 8-bit Ports as Port-0,Port-1, Port-2, Port-3. Each port has a latch
and driver (or Buffer).
The
alternate function of Port-0 lines as multiplexed low byte address/data lines.
The
alternate function of Port-2 lines as
high byte address lines.
The
alternate function of Port-3 as control signals. Port-1 does not have any
alternate function.
There
are 21 internal registers in SFRs. The SFRs are mapped as internal data memory.
The data memory address space 80H to FFH.
The
8051 has 8-bit ALU: to perform Arithmetic and logical operations on binary
data. The A & B registers are used to hold the input data and the result of
ALU operation.
The
PSW store the Status of the result of ALU operations. It contains 4 Math flags
& 2 register bank select bits.
The
Controller will fetch the instructions one by one and starting address is stored in PC & Stored in IR.
Which decodes the instructions and give information to Timing & Control
Unit.
An
external quartz Crystal is connected for clock generation.
By
using 16-bit programmable timer/counter they can count the number of high to low transitions of
the signal applied to the timer pins.
8051 family of microcontrollers has a full
duplex Serial port , can be programmed to work in any one of four operating
modes as Mode-0, Mode-1, Mode-2, Mode-3
There
are 128 bytes of RAM inside the 8051 µc with 00H to 7FH address. These 128
bytes are divided into three different
groups as
1. 32 bytes from 00H to 1FH locations are set for
register banks and stack.
2. 16
bytes from 20H to 2FH are set for bit-addressable RAM.
3. 80
bytes from 30H to 7FH are used for read
and write storage or scratch pad.
The
PCON register is used for power control and baud rate selection. It also
consists general purpose user flags.
TMOD
register is used to select the operating mode and the timer/ counter .
TCON
register consists of timer over-flow flags, timer run control bits, external
interrupt flags and external
interrupt type control bits.
Including
RESET there are 6 interrupts in 8051 µC.
IE
register is used to enable or Disable the interrupts of 8051.
IP
register can be programmed to make the priority of interrupt .
SBUF
register is to hold the data. SCON controls data communication register, PCON
controls data rates .
***Write a short note on
Register Banks and Stack
There
are 128 bytes of RAM inside the 8051 Microcontroller from 00H to 7FH. These 128 bytes are divided into
Three different groups as
1. 32
bytes from 00H to 1FH are set for register banks and Stack.
2. 16
bytes from 20H to 2FH are set for bit-addressable RAM.
3. 80
bytes from 30H to 7FH are used for read
and write storage or scratch pad.
These
80 locations of RAM are widely used for the purpose of storing data and
parameters by 8051 programmers.
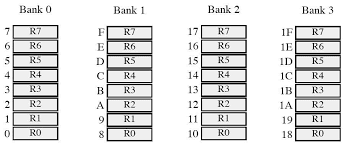
A
total 32 bytes of RAM are set for the register banks and Stack. These 32 bytes
are divided into 4 banks of registers.
Each
bank has 8- registers RO to R7
RAM locations from 00H to 07H are set as Bank0, 08H to 0FH are set
as Bank1, 10H to 17H are at as Bank2 & 18H to 1FH are set as Bank3.
Bank
1 uses the same RAM space as the stack . This is a major problem in programming
the 8051.
We
can Select the banks by using PSW bits D3 & D4 (RS0
&RS1 ). The particular register bank is selected by the
bit addressable instructions SET B & CLR.
Eg:
SET B PSW.3
*** Explain Memory
Organization of 8031/8051.
A
Micro controller based system require both EPROM and RAM. The EPROM is required
for permanent program and permanent Data storage.
The RAM is required for temporary Data storage
and Stack. The 8031/8051 has 64K bytes program memory & 64 K bytes Data
memory.
The
Microcontroller can only read from program memory. PSEN bar Signal is used for
reading the program memory. ROM / EPROM
/ EEPROM are used as program memory.
The
microcontroller can read and write with data memory . RD bar & WR bar
signals are used for reading and writing the Data memory. Static RAM can be
used as Data memory.
In
8051 micro controller the entire 64 Kb data memory space is external . It’s
address is 0000H to FFFFH.
A
part from external data memory, the 8051 has 256 bytes of internal data memory
in which the first 128 bytes are called Internal RAM & next 128 bytes are
called SFR. The address range of SFR’s & internal RAM are 00H to FFH.
The
8051 has 4 Kb internal ROM can be mapped to first 4Kb address space of program
memory if EA pin is High.
The address of internal ROM is 0000H to 0FFFH.
The usage of internal ROM is optional. The external program memory 60Kb address
range is 1000H to FFFFH. Remaining program memory.
When
EAbar pin is low the entire 64 Kb program memory 0000H to FFFFH is treated as
external memory. i.e internal 4Kb ROM cannot be accessed.
By
using this 16- bit pointers we can
address 216 =64 Kb. Memory
locations. Hence 8051/8031 supports two memory banks of 64 Kb each, one for
program and the other for data.
EA (External access)
Used to read program from external memory.
When EA bar is connected to ground (logic-0) then entire 64Kb is used
as external (EPROM/RAM) memory.
If we want to read from external
memory then EA bar is connected to GND that means EA=5V or 1.
If we use only internal memory then we connect EA bar to Vcc (5V)
Means EA=0V.
When
EA bar is connected to Vcc (logic-1) the first 4 Kb of program
memory is refer to internal ROM (4Kb) & remaining 60Kb is to external
(EPROM/RAM). Memory.
To
minimize the cost & when memory requirement is less then single memory is
used for both data & Program.
When
a single memory bank is provided then the read control signal is generated by
logically ANDing the PSEN and RD signals.
When
a single bank is provided then system designer has to partition the total 64 Kb
of address space for program and data. Then the 256 bytes internal memory can
be accesses as data memory by using 8-bit address.
The 8051 microcontroller does not provide
separate I/O addresses. Therefore in 8051 based system only memory mapped I/O
is possible. Hence some of the memory address space should be reserved for I/O
devices.
*** Explain 8051 Port
Organization
Port Organization:
The port is a buffered IC which is used to hold the data transmitted from the microcontroller
to I/O device (OR) vice versa.
In
8051 Microcontroller there are 4 ports P0, P1, P2
and P3. Each port is a 8-bit bidirectional port. Each pin in a each
port has a D-type output latch.
There
are 3 components in the structure. They are (1). D-latch (2). Output driver
(3). Input buffer
Port-0 pins are used for
inputs and outputs. When 8051 is connecting to an external memory then port-0
used for both address and data bus. i.e AD0 – AD7 .
When
ALE=0 then port-0 works as data bus. (D0-D7 ). When
ALE=1, then port-0 works as lower order Address bus A0-A7 .
Therefore ALE is used for demultiplexing address and data with the help of a
Latch (74LS373).
When 8051 is not connected to external memory
then port-0 pins must be connected externally to 10K-ohm pull-up resister.
This
is due to that P0 is an open
drain with external pull-up resistors port-0 can be used as simple I/O port.
Like P1, P2 , P3 ports.
P1,
P2 , P3 ports do not need any pull-up resistors
because they already have pull-up resistors internally.
Port-1 and Port-2 are
used as simple I/O. When external memory is connecting Port-2 must be used as
higher order address bus A8 –A15 .
Port-
2 along with port-0 provide 16-bit address bus. By using this 16-bit address
lines 8051 can access 64-Kbytes of external memory.
Port-3 can be used as input
or output port-3 also does not need any pull-up resistors as port-1 and port-2.
When
8051 is connecting to an external memory then port-3 provides some control
signals as P3.0 and P3.1
are used for RXD & TXD Serial
communication signals. P3.2 &P3.3 are INT0 & INT1 for external interrupts.



















Mam we need flow charts for ALP programs 4th unit please
ReplyDelete